| |
|
|
History of Western Philosophy |
|
| |
| |
|
|
|
| Plato & Aristotle (closeup
from School of Athens by Raphael) |
|
 |
|
 |
|
Triumph of Thomas Acquinas (with
Aristotle and Plato, over Averroes)
by Benozzo Gozzoli, 1471 |
|
 |
| Creation of the sun and
moon, one of nine ceiling panels of Sistine
Chapel, by Michelangelo |
|
 |
| Dream of St. Helene
by Paolo Cagliari, c. 1580 |
|
 |
|
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
by Sir Peter Paul Rubens |
|

|
| Martin Luther nails the 95
Theses to the door of Wittenberg Cathedral- Oct. 1517. Painting, 1872,
by Ferdinand Pauwels |
|
 |
|
The Doubting of
St.Thomas-
late 1590s by
Michelangelo Merisi da Caravaggio.
(Tenebrism, extreme chiaroscura) |
|
 |
Louis XIV
(age 63)
by Hyacinth Rigaud, 1701 |
|
 |
| Blinding of Samson
by Rembrandt van Rijn, 1636 |
  |
|
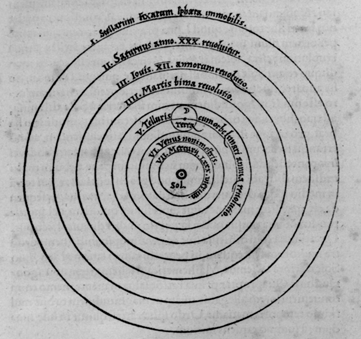
Nicholas Copernicus, Polish humanist and astronomer, set
out to prove Ptolemy’s system - that planets revolved around Sun |
|
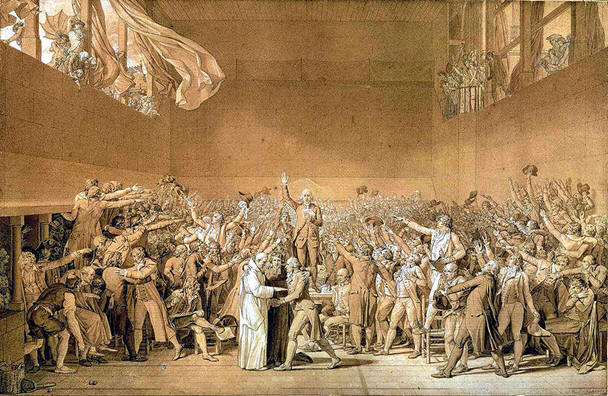 |
| Tennis Court Oath
June 20, 1789. French Revolution. Artist Jacques-Louis David |
|
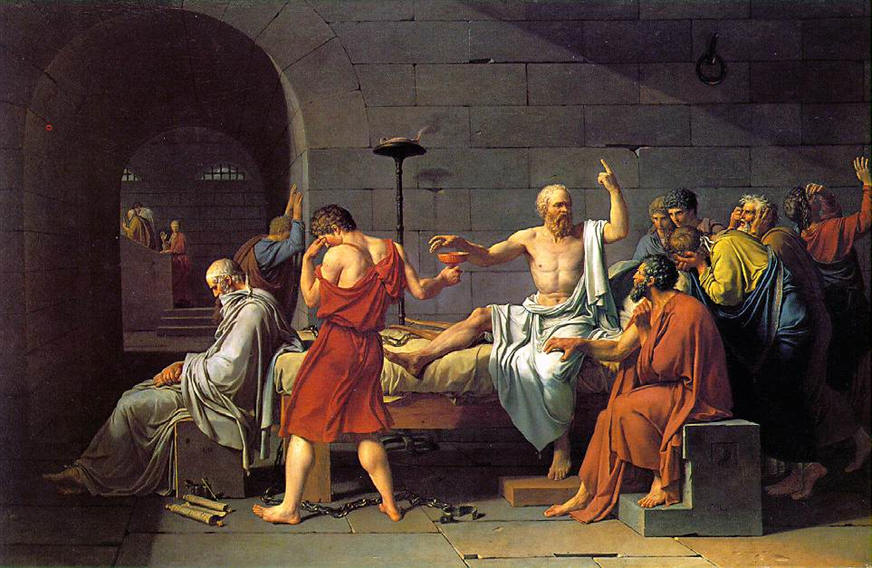 |
| The Death of Socrates
by Jacques-Louis David, 1787 |
|
 |
|
Madame de Pompadour as Venus
by Francois Boucher, 1756 (Rococo) |
|
 |
|
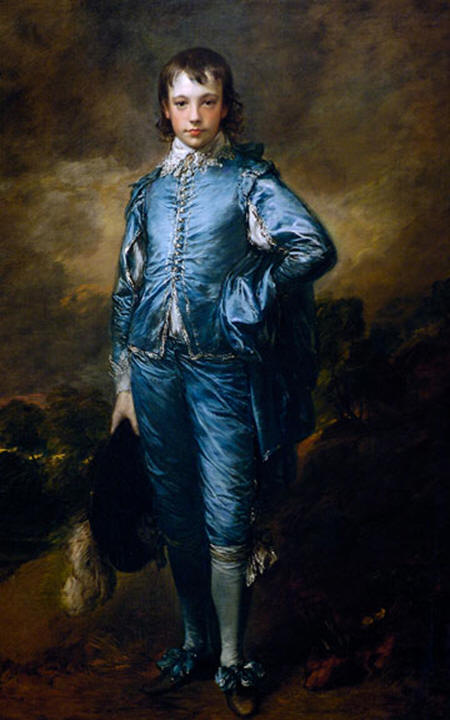
Blue Boy
by Thomas Gainsborough, 1770 |
|
 |
|
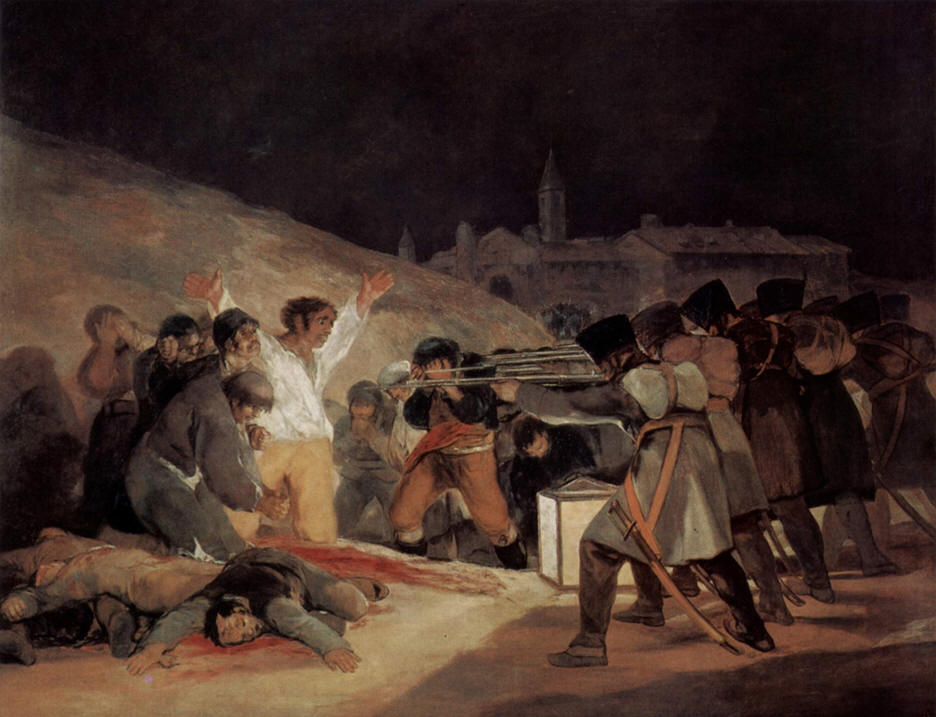
Executions of The Madrilenos
Defenders of Madrid, on the Third of May, 1808
by Francisco Goya |
|
 |
|
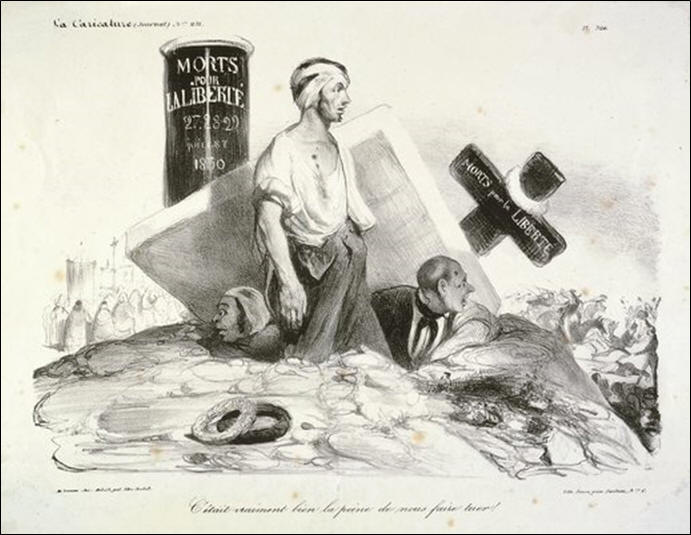
Honoré Daumier: 1830, ghosts of
original French Revolution, aghast that the current state of France
is what they died for . . . |
|
 |
|
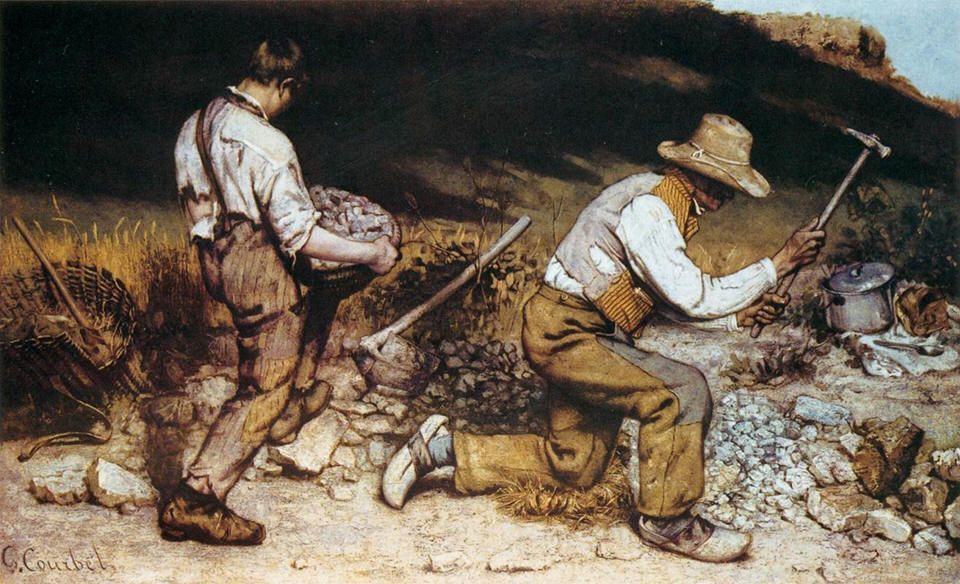
The Stone Breakers
by Gustave Courbet, 1849 |
|

|
|
The Persistence of Memory
by Salvador Dali 1931
(Surrealism) |
|
 |
|
The Ladies of Avignon,
1907. by Pablo Picasso |
|

German & Spanish bombing attack of
Guernica, Spain 1937
by Pablo Picasso |
|
 
German & U.S. Propaganda |
|
   |
|

|
|
Willen de Kooning's Woman I
(1950-52). It was one of a series of six oil-on-canvas paintings
centered upon a single female. |
|
 |
|
Poet on a Mountaintop
Shen Zhou, ca. 1500 (China) |
|
 |
|
The Great Wave off Kanagawa
by Hokusai Katsushika (1760-1849)
series:
Thirty-Six Views of Mount Fuji
Mt. Fuji, symbol of enduring beauty and stability; it is
dwarfed by a giant, threatening wave: it is contrasted with the
fragility of life. (JAPAN)
|
|
 
|
|
Japanese Kabuki Theater |
|

|
Samurai sword, most favored weapon
JAPAN (artist unknown) |
| |
|
|
Humanities Lectures: This lecture series, developed by Susan Fleck,
is an integrated approach, looking at the History, Philosophy, Literature,
Music, and visual Arts - Painting, Sculpture & Architecture: From the
Renaissance era thru mid- 20th century. The focus is on Western
Civilization: There are two lectures at end about the East- a sweeping
overview of China and Japan. This was created for a course on World Humanities that Susan taught at a community college in Florida. (See notes below about
viewing the Power Point presentations.)
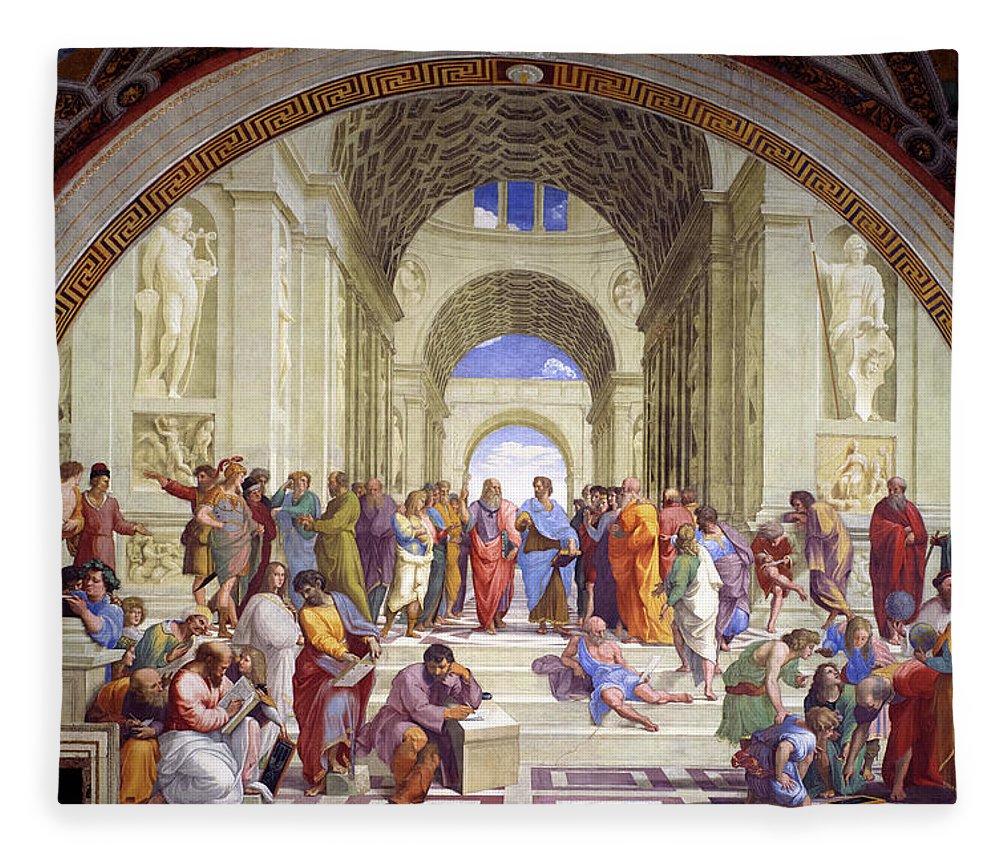 School of Athens by Raphael
School of Athens by Raphael
*
NOTEs - for viewing Power Point
presentations:
*** For Power Point slides: DO NOT use
the "Next" arrow to advance to next slide. Some slides have
'animation': Click
within the main body of the presentation window to advance lines
of text/animation (otherwise, slide may look blank, or partially
filled, with just a heading. (The "Next" arrow just advances to next
slide, without advancing text or other data within a slide.)
*** Click on
"NOTES" tab - right hand side of presentation (versus "outline" tab): There
are detailed notes on some of the slides explaining the slide images, along
with additional narrative.
*** Many Links to other
website pages within the slides are no longer be valid - these presentations
were prepared around 2010
*** The WORD
documents are notes that go along with the Power Point slides'
presentation.
|
POWER POINT Presentations |
WORD documents |
|
1.
Humanities Course Introduction: ART "appreciation:" How to
'Look" at Art. What is History? What is Philosophy? These questions
are explored. |
1.
Humanities Course Intro |
|
2.
Ancient Greek Philosophy: Pre-Socratics, Socrates, Plato,
Aristotle. We begin here, because it was Western contact with the
Arab Scholars who preserved and commented on these ancient texts:
this precipitated coming out of the Dark Ages. |
2.
Ancient Greek Philosophy |
|
3.
Medieval Era Survey: Philodophy of Church Theologists and
culture leading up to the Renaissance. Double Truth Theory. A comparison of Medieval to
Renaissance Art. |
3.
Medieval Era Survey |
|
4.
Early Italian Renaissance: 15th Century: History, Philosophy, Architecture:
Religiosity coexists with Secular; Capitalism; Exploration of
Americas; Science & Technology; Printing Press; Development of
Nation States; Emphasis on Humanism & Rational Thought |
4.
Early Italian Renaissance |
|
5.
Italian Renaissance Painting: Masaccio, Piero della
Frencesca, Fra Angelico, Leoardo da Venci, Raphael, Michelangelo |
5.
Italian Renaissance Painting |
|
6.
Renaissance Sculpture: Ghiberti, Donatello, Michelangelo,
Properzia de' Rossi |
6.
Renaissance Sculpture |
|
7.
Renaissance Music & Literature: Music forms and terms.
Composers: Guillaume Dufay, Heinrich Isaac, Jasquin des Prez.
Literature: Francesco Petrarch, Baldassare Castiglione, Niccolo
Machiavelli. |
7.
Renaissance Music & Literature |
| 8.
Venetian Renaissance & Mannerism in Europe: 16th
Century: Architecture:
Jacobo Sansovino, Andrea Palladio - "Four Books of Architecture."
Venetian oil painting: Titian, Cagliari. Mannerism:
Painters and Sculptors, living in the shadow of early Renaissance
giants, dramatically depart in the manner of style, e.g., the
style of Raphael. Several artists are reviewed, e.g. Celline
& El Greco. |
8.
Venetian Renaissance & Mannerism in Europe |
|
9.
North Europe Early Renaissance: 15th Century: Germany,
France, England, the Lowlands: History &
culture leading up to 15th Century; Printing Press invented;
Turbulent times - Holy Roman Empire; Characteristics distinguishing
Art from Italian Renaissance. Artists: Robert Campin, Jan Van Eyck,
Rogier van der Weyden, Hieronymus Bosch. |
9.
North Europe Early Renaissance |
|
10.
North Europe High Renaissance: 16th Century: History & Architecture: Holy
Roman Empire- Emperor Chaarles V; France- King Francis I; Spain-
King Philip II. Painting: Hans Holbien the Younger, Pieter Bruegel
the Elder, Quentin Massys, Albrecht Durer |
10.
North Europe High Renaissance |
|
11.
Protest and Reform in Northern Europe: 16th Century: Background for
Protestant Reformation; Catholic Church abuses; new merchant
class; early dissenters; Christian Humanism; role of printing press;
Disiderious Erasmus, Monk- "In Praise of Folly;" William Tyndale;
Martin Luther "95 Theses;" peasants' revolts; John Calvin; other
protestant off-shoots; Hussite wars. |
11.
Protest and Reform in Northern Europe |
| 12.
England: Reform & Renaissance- 16th Century: Reform: Hundred Years War
with France; War of Roses; Tudor England; Henry VIII & Reformation
Parliament; Anglican Church - King is supreme leader; Dissent &
uprisings; Queen Mary, Queen Elizabeth I, Catholics, Puritans,
Common Book of Prayer; English Civil War (England & Ireland).
Renaissance: Age of Shakespeare - Elizabethan Era; Literature,
Philosophy & Music dominate the Arts; Literature: Geoffrey Chaucer,
Edmuch Spenser, William Shakespeare; John Milton, Sir Thomas More,
Sir Francis Bacon, & many more; Music: Madrigals & Sonnets;
Architecture: not much new. |
12.
England: Reform & Renaissance |
|
13.
Catholic Counter-Reformation: 16th Century: This
is a series of actions lasting about 100 years to counteract the
Protestant Reformation; Catholic Reformation Goals; Coucil of Trent;
Reaffirmation of doctrines, Control by extreme censorship &
Inquisitions; New Religious Orders; Political / Religious Wars:
France, Spain, Germany; Remake Rome as Cultural Center: specific
decrees about ART- 'arouse piety and ferver,' 'clarity' in music &
literature, counter Mannerism. |
13.
Catholic Counter-Reformation |
|
14.
Art of the Catholic Counter-Reformation: 16th & 17th Century:
Michelangelo - Sistine Chapel, Mannerist Painting; Baroque Era -
Church in Rome; Italian Baroque painting: Caravaggio, Artimisia
Gentileschi, Annibale Carracci, Fra Andrea Pozzo; Architecture &
Sculpture: Bernini's Piazza San Pietro, Bernini's David,
St. Teresa in Ecstasy; Baroque Music. |
14.
Art of the Catholic Counter-Reformation |
| 15.
Aristocratic Baroque Art: 17th Century: Peter Paul Rubens:
accepted the two towering institutions: Absolute Monarchy & Roman
Catholic Church; 21 paintings about Marie de' Medici's life;
Rubenistes - favored Ruben's style). Nicolas Poussin (Poussinistes -
favored classical lines). Louis XIV - The Sun King- Control over
everything, including Art & Architecture: Royal Academy - absolute
standards; Versailles Palace - enormous structures. |
15.
Aristocratic Baroque Art |
|
16.
Aristocratic Baroque: Palace of Versailles: Lots of pictures
and diagram of this enormous complex of structures, fountains,
sculptures, gardens. |
|
| 17.
Baroque Music & Literature: 17th Century: Baroque music
outside of Italy: Handel and the Oratorio, Johann Sebastian Bach.
Literature: Moliere and the Baroque Stage, John Donne, John Milton,
Miguel de Cervantes. |
17.
Baroque Music & Literature |
| 18.
Northern Baroque Art: The Netherlands: 17th Century: Holland
- Protestant, Flanders - Catholic. Holland: Impact of Protestant
Reformation: Distinct form of Baroque Painting; large demand for
paintings; Huge number of painters - had to specialize/ 5 categories
(e.g. portraits, landscape, still life). Painters: Frans Hals,
Judith Leyster, Jan Vermeer, Rembrandt van Rijn, Rachel Ruysch. |
18.
Northern Baroque Art: The Netherlands |
|
19.
Scientific Revolution & 17th Century Philosophy: BIG IDEAS:
The discovery of new knowledge and the questioning of tradition.
Science: Science needed tools and "freedom." Why was the
Church in denial? Heliocentric (sun-centered) theory (3rd c. BC) vs
Geocentric (earth-centered) theory accepted by The Church;
Ptolomy 140 CE - planets revolved around Sun. Nicholas Copernicus
set out to prove Ptolomy's system; Tycho Brahe, Astronomer; Galileo,
mathematician/ scientist - improves telescope; Johannes Kepler,
Astronomer; Isaac Newton, Mathematician, Astronomer, "Mathematical
Principles of Natural Philosophy;" Invention of microscope; World
Exploration. Philosophy: Empiricism vs Rationalism; Francis
Bacon (Empiricism); Rene Descartes (Rationalism, Father of Modern
Philosophy); Thomas Hobbes (politics/government); John Locke
(anti-authoritarian - influenced U.S. founding fathers). |
19.
Scientific Revolution & 17th Century Philosophy |
| 20.
Enlightenment & Revolutions: 18th Century: Enlightenment,
American Revolution, French Revolution, Industrial Revolution,
continuation of Scientific Revolution. Emphasis on mind's power to
reason, in contrast to beliefs based on religious
faith. Optimism - Humans can make progress. Political thinkers:
Hobbes, Locke, Voltaire, Rousseau, Diderot, Paine ("Common Sense"),
Jefferson, Franklin. Intellectuals: world wide exchange of letters.
American and French Revolutions discussed; Napoleon; Legacy from
Revolutions; How the Industrial Revolution changed the world; Adam
Smith - the Free Market system; New Sciences defined - geology,
mineralogy, zoology, biology; Diderot's Encyclopedia; Linnaeus's
Biology Classification system; belief that Humans could eventually
know and catalogue everything!! |
20.
Enlightenment & Revolutions |
|
21.
18th Century Neoclassicism Arts & Literature: Pouissin's
intellectual classicism should help restore orderliness and be
corrective influence on social ills. By mid-century, grandiose
history subjects were desired. Diderot and others hated Rococo
fantasies. Public-minded values of Greek and Roman heroes.
Jacques-Louis David - unchallenged Painter of French Revolution;
Painters Angelica Kauffmann, John Copley; Sculpture - Jean-Antoine
Houdon; Neoclassic Architecture, including U.S. Literature:
Johnathan Swift, Voltaire, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Mary
Wollstonecraft- women's rights, a hot topic; Rise of The Novel -
Jane Austen, Daniel Defoe. Rise of the public consert: Symphony,
Franz Joseph Haydn, Wolfgang Mozart, Beethoven. |
21.
18th Century Neoclassicism Arts & Literature |
| 22.
Rococo in France, Sensibility in England: 18th Century: France:
rocaille, stones & shells used to decorate; ornate, fussy details,
not dark & grandiose like Baroque; Rococo interiors- hotels, salons;
Age of Louis XV- Paris Salon exhibits, Salon at Palace of Louvre, 8
Rococo painters. England: Rococo is too frivolous; Painters -
refined, elegant style; English satire- William Hogarth, Sir
Joshua Reynolds, Thomas Gainsborough. Portraits and
Landscapes. |
22.
Rococo in France, Sensibility in England |
|
23.
Romanticism: History, Philosophy, Literature, Music: 19th
Century: Philosophers: Jean-Jacques Rousseau -
exploration of the self; George Friedrich Hegel - comprehensive
philosophical system, how Absolute Spirit manifests itself,
Universal Mind; Immanuel Kant - cannot know 'the thing in itself,'
Transcendental Idealism, Categorical Imperative (DUTY), Ralph Waldo
Emerson - American Transcendentalism (rooted in Kant), union of
humaity with nature; Henry David Thoreau - author, poet,
abolitionist, civil disobedience. History: Abolitionism in
U.S.- Participants; Civil War - why the Union won, an Industrial
War, Consequenses. Literature: Subjects; Melville, Blake,
Stevenson, Goethe, Bronte, Doyle - The Mystery Tale, Wordsworth,
Whitman. Music: The most "romantic" art form? Expansion of
techniches to enhance emotion; Technology advances; Operas, Lied,
Chopin solos, Program Music; Examples: Berlioz, Brahms,
Chopin, Verdi, Wagner, Tchaikovsky. |
23.
Romanticism: History, Philosophy, Literature, Music |
| 24.
Romanticism: Wars, Painting & Architecture: 19th Century:
Napoleonic Wars, throughout Europe - unprecedented scale
- extreme death, sickness, destruction ; takeover, then defeat;
Consequences. Romanticism: Attitude over Style -
Enlightenment 'reason' too cold and emotionless; subjective
experience; glorification of the self and originality; Romanticism
main subject matter. Artists: Jacques-Louis David, Eugene
Delacroix, Francisco Goya, Theodore Gericault, Joseph Turner, Jean
Leon Gerome, John Constable, Thomas Moran, Casper Friedrich.
Architecture: Revival of earlier styles and modern engineering. |
24.
Romanticism: Wars, Painting & Architecture |
|
25.
Realism: Industrial Revolution: History & Philosophy:
18th &19th Centuries: The Industrial Revolution changed how
the world produced goods; changed societies from agricultural to
industry; rapid growth of textile industry in England; rapid growth
of cities; invention of steam engine; development of transportation
& communication; Captains of Industry; Adam Smith: Classical
Economic Theory; legislation to protect workers, children; Charles
Dickens - wanted reform (Ebenezer Scrooge); Socialism - attempts at
utopian communities; Karl Marx & Friedrich Engels: "Communist
Manifesto;" George W. F. Hegel, philosopher, origin of Marx's ideas:
dialectic logic; Main concepts in Communist Manifesto; Social
Darwinism. |
25.
Realism: Industrial Revolution: History & Philosophy |
|
26.
Realism: Painting, Photography & Literature: 19th Century:
Accurate, objective portrayal of reality, including the sordid &
seamy.
Honoré Daumier -Painter
& Lithographs used in newspapers attacking the gov’t, ridiculing
lawyers, and social & intellectual pretentiousness. Louis
Napoleon Bonaparte, nephew of 1st Emperor: coup de'etat-
Dictator Napoleon III; Transformation of Paris - poor are displaced.
Other Painters: Gustave Courbet, Edouard Manet, Alexandre
Cabanel, Thomas Eakins, Winslow Homer: Wood engravings, Painter.
Photography: Matthew Brady - Documents U.S. Civil War.
Literature: Honore de Balzac - panorama of French life after
fall on Napoleon (1815); Gustave Flaubert; Emile Zola; George Eliot
(Mary Ann Evans); Charles Dickens; Fyodor Dostoyevsky. |
26.
Realism: Painting, Photography & Literature |
| 27.
Early 20th Century: History, Philosophy, Arts- Avant Garde:
Many ISMs. History: American- Manifest Destiny. WWI, Treaty
of Versailles. A New Russia: Lenin & Stalin. Science &
Technology: inventions-Communications, Transportation,
Housekeeping; Einstein-Theory of Relativity; Structure of Atom;
Helmholz- conservation of energy. Nietzsche-
antiauthoritarian. Sigmund Freud- father of psychoanalysis.
Avant Garde: pushing bounds of what considered norm:
Impressionism (and post-), Fauvism, Cubism, Futurism, German
Expressionism, Dadaism, Surrealism, DeStijl-ism, Abstractionism.
Modern Architecture, first skyscraper. Featured Artists:
Claude Monet, Henry Matisse, Pablo Picasso, Otto Gutfreundi, Sonia
Delauney, Gino Severini, Emil Nolde, Vassili Kandinsky, Igor
Stravinsky, Frank Lloyd Wright. |
27.
Early 20th Century: History, Philosophy, Arts- Avant Garde
Raw notes |
| 28.
American Modernism- Painting; Modernist Music & Literature;
Repression, Deptression, New Deal: Early 20th Century: Science:
Pursuit of the Atom. Artists & Writers: Georgia O'keeffe,
Charles Demuth, Edward Hopper, Thomas Hart Benton (murals), Jacob
Lawrence, Sergei Eisenstein (film), Louise Dahl-Wolfe (photography).
Ezra Pound, T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, Virginia Woolf, Ernest
Hemmingway, William Faulkner. Repression: Facism & Communism:
Benito Mussolini, Adolf Hitler, Francisco Franco. U.S. Panics,
Recessions, Depressions: 1857 - 1940; Dust Bowl & Drought
1930-36+. Political Progressivism: Theodore Roosevelt,
Woodrow Wilson, Franklin D. Roosevelt; Trust busting, Square Deal,
Fed. Reserve Act, Progressive Income Tax, New Deal, Huge new gov't
agencies, 1938 unemployment 19%, Social Security, Propaganda &
Fireside Chats. Art as Propaganda: Russia, Germany, U.S.
American Music: Prairie-Cowboy Songs, South- gospel, New
Orleans- Jazz. Charles Ives, Aaron Copland, George Gershwin, Scott
Joplin, Louis Armstrong, Duke Elington, |
28.
American Modernism- Painting; Modernist Music & Literature;
Repression, Deptression, New Deal |
| 29.
Mid-20th Century: History: WWII: Winston
Churchill, the Pacific- Japan, Atom bomb, Holocaust, Aftermath
consequences. Cold War, Spread of Communism, Cuban Missle Crisis
1062, Vietnam Wars, Space Race. Philosophy- Existentialism:
subjective and personal dimension of human life: individuals
struggling with apparent meaningless of life. Frederich Nietzsche
('father of'), Soren Kierkegaard, Jean-Paul Sartre, Albert Camus,
Simone de Beauvoir (study of women: they need to break habit of
being seen only in relation to men: The Second Sex).
Objectivism: Ayn Rand's comprehensive philosophy - to counter
all major philosophers' false dichotomies. Individualist, Author of
fiction (Atlas Shrugged, The Fountainhead), and non-fiction
articles, speeches. 60's Movements: e.g. Pacifism,
Environmentalism, Women's Liberation, Counterculture (hippies).
Abstractionism in American Art: Limit of 'pure abstraction'
reached peak in 1940's & 1950's: Jackson Pollock, Lee Krasner,
Willem de Kooning, Mark Rothko, Alexander Calder, Isamu Noguchi.
Consumer Culture / Pop Culture: Artists turned their attention
to consumerism (TVs, Cars, Shopping Centers): John Cage, composer;
Robert Rauschenberg (messy art), Louise Nevelson (boxes), Andy
Warhol, TV cartoons, Roy Lichtenstein, Donald Judd, Sol LeWitt,
Bridget Riley, Norman Rockwell, Christo & Jeanne-Claude (grand scale
environmental art), Frank Gehry (Architect). Music: Andrew
Lloyd Weber (16 musical plays- half made into movies),
Rock-and-Roll: Elvis Presley, many other 'greats,' American
Bandstand TV. |
29.
Mid-20th Century |
| 30.
Chinese Civilization after the 13th Century: Dynasties:
Yuan Dynasty (1279-1368): Kublai Khan; quiet resistance to foreign
rule; Chinese seals. Ming Dynasty (1368-1644): orderly gov't &
social stability; mandarin scholar-bureaucrats, enormous building
projects- incl. Forbidden City; Grand Canal; 20th century history:
early chaos, Chiang Kai-shek, Communist Party re-org under Mao
Zedung: Mao's "Great Leap Forward" (catastropy), Mao the murderer:
'Cultural Revolution'; Chinese Capitalism. Religions:
Confucianism, Taoism, Buddhism (Sidhartha Gautama), ancestor
worship, Christianity. Culture & Arts: Ming furniture,
Gardens & Rock Sculpture, Scholar's Rocks, Jade Carving, Literati
Painting, Calligraphy, Embroidery Art, Poetry (extreme high regard
for poetry), Tiananmen Square Massacre, Music - Pipa & Beijing
Opera. 'freedom' for artists now? |
30.
Chinese Civilization after the 13th Century |
| 31.
Japanese Culture after the 15th Century: Land of the Rising
Sun. History: Feudal waring states era 1477-1600: Shogun
(military leader);
Edo (Tokyo) Period 1600-1867: period of stability and unification;
Isolationism edict; Samuri, top rung of society; 1850s trade and
knowledge of the West begins; Meiji Era - close gap with the West;
Industrialization, Universal Education. Sino-Japan & Russo-Japan
wars; Expansion in East Asia; WWII Attack on Pearl Harbor, atomic
bombs, surrender; Turned to economic, versus military means to
achieve power & influence. Religion: Confucian, main
philosophy; Mahayana branch of Buddhism entered 6th Century-Tokugawa
Shogunate controlled Buddhist clergy; 1191 Zen Buddhism entered from
China; 1542 Portuguese introduced Christianity (and guns);
Shinto resurrected as a state religion during Edo period - practiced
only in Japan; 90,000 Shinto Shrines; Shinto & Buddhism compatable-
linking of gods; Revival of Shinto brought revival of bushido (“Way
of the Warrior”) code of conduct for samurai (strongly Confucian in
nature);
1868:
feudal era ended, samurai class abolished.
ARTS: Haiku Poet Basho, Zen master Hakuin, & Zen Chinese
ink-style painting
traditions; Landscape Painting. After 1600 Zen masters created
paintings, poems, & calligraphy for followers, not for “decoration.”
Koan (Zen riddle), Woodblock Prints, The Japanese Garden.
Literature (in addition to poems): (from 1868) Modern fiction,
"confessional novel." Theater: Noh- Dances, dialogue,
songs by main actors, music from a ji (chorus); Bunraki - Japanese
Puppet Theater (not for kids); Kabuki Theater; Geisha - artist
entertainers; Japanese Anime; Japanese Cultural Impact: Influenced
many famous western artists. |
31.
Japanese Culture after the 15th Century |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
xx
xx
|

































 School of Athens by Raphael
School of Athens by Raphael